Yogyakarta, 15th January 2026 — Water is a fundamental element for human survival and a basic necessity in daily activities such as cooking, bathing, and drinking. Along with population growth, the demand for clean water continues to increase, while its availability remains limited and vulnerable to decline if exploited excessively. Therefore, sustainable water resource management is essential to support community welfare.
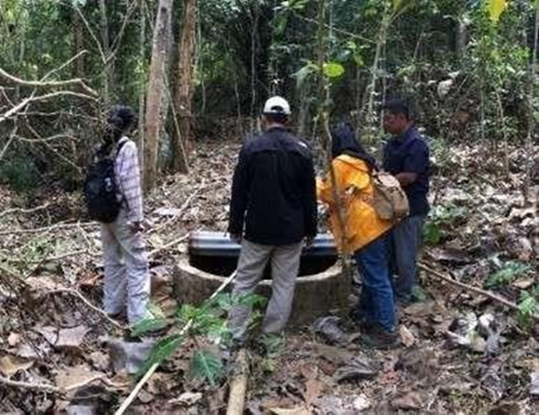
One of the main sources of clean water in mountain areas is spring water, namely groundwater that naturally emerges to the surface and forms a concentrated flow. Springs are widely utilized by communities to meet both domestic and non-domestic needs, including agriculture and livestock. This condition is also found in Kapanewon Dlingo, Bantul Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta, where most areas rely on spring water as a primary source of clean water.
In response to this condition, a research team from the Environmental Management Master’s Program, Graduate School of Universitas Gadjah Mada (SPs UGM) conducted a study to analyze the potential of spring water as a source of clean water using a hydrogeomorphological approach. The study was led by Dr. Langgeng Wahyu Santosa, S.Si., M.Si., with team members Dr. Agus Joko Pitoyo, S.Si., M.A. and Ermina Pradipta Darmastuti.
The hydrogeomorphological approach was applied to examine the relationship of geomorphological aspects—such as landform genesis, slope morphology, morphoprocesses, morphostructure, and morphochronology—and the characteristics of a surfaced spring. The analysis involved field surveys, measurements of discharge and flow characteristics, as well as water quality testing based on parameters including temperature, pH, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), and electrical conductivity (EC). A scoring assessment was conducted to determine the potential of springs as primary sources of clean water in the study area.
The principal investigator, Dr. Langgeng Wahyu Santosa, explained that the hydrogeomorphological approach provides a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between the physical conditions of the area and water resource availability.
“The hydrogeomorphological approach allows us to comprehensively understand the relationship between landforms and spring characteristics. With this understanding, spring water potential can be managed more appropriately, sustainably, and based on scientific evidence to support community water needs,” he said.
The results show that the study area consists of three landform units: the Old Volcanic Faulted Structural Hills of the Nglanggeran Formation, the Tuff Conglomerate Faulted Structural Hills of the Sambipitu Formation, and the Solutional Karst Hills of Reef Limestone of the Wonosari Formation. Across these three landform units, a total of 123 spring points were identified, evenly distributed across six villages.
Most of the identified springs are perennial, flowing throughout the year and not influenced by seasonal changes, while only four springs are intermittent, flowing periodically during the rainy season. The total measured spring discharge reaches 138,169.81 cubic meters per year. However, the analysis also indicates that this availability is still insufficient to meet the total community water demand for agriculture, livestock, and domestic uses, which amounts to 17,509,790.22 cubic meters per year, resulting in a water scarcity condition.
The study also highlighted water quality aspects. Several springs were found to exceed quality standards for certain parameters, including TDS, turbidity, color, COD, BOD, and total coliform at specific locations. These findings create an important basis for developing more sustainable spring management strategies.
The research team recommended several management strategies, including the construction of water storage reservoirs to collect excess water during the rainy season, protection of spring areas within a 5–10 meter radius, establishment of community-based spring management groups, education on maintaining spring protection infrastructure, regular water quality monitoring, reduction of excessive use of manure-based fertilizers, and the provision of adequate sanitation facilities for local communities.
SDGs Keywords: SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation, SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy