Initially, threats to the country were only considered from a military aspect. However, global developments indicate multidimensional threats, including Military, Politics, Economy, Environment, etc.
The concept of security in Indonesia, viewed from its scope, encompasses international security, regional security, collective security, national security, national defense and security, domestic security, public order and security (Kamtibmas), human security, maritime security, aerospace security, cyber security, etc.
When compared to concepts that apply at the international level or in many countries, defense is understood as a function aimed at safeguarding and protecting national security or is identical with national security, and even broader, with the goal of national security.
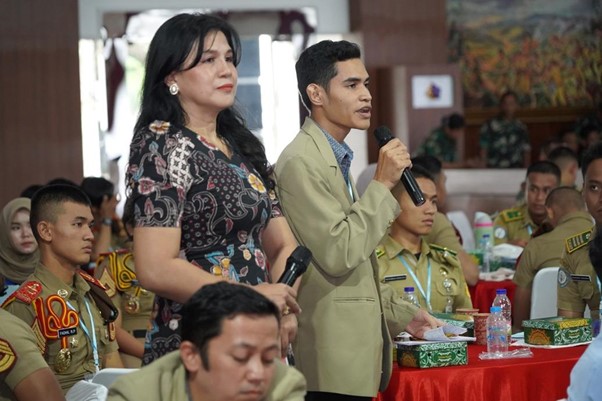
This was stated by Prof. Dr. Armaidy Armawi, Chief of the National Defense Program at the Graduate School of UGM. He was the first speaker in the seminar titled Bureaucratic Reform in the Era of Society 5.0 to Improve Public Service Quality, held at the Moch. Lily Rochali Building of the Military Academy in Magelang on Wednesday, February 19th 2025.
Prof. Armaidy also conveyed three points regarding Indonesia’s security concept:
- To safeguard the ideology and basic values, including democracy.
- The interest in maintaining sovereignty and territorial integrity (military interest).
- The interest in strengthening the nation’s economy (economic interest).
- The interest in helping to shape a peaceful, just, and prosperous world order (international interest).
Meanwhile, the National Security Council has strategic objectives to ensure that national security priorities, civil defense emergency management systems, and intelligence systems are led, coordinated, and well-managed.
According to the National Security Council, a holistic and integrated approach to managing national security risks, known as “4R,” includes:
- Reduction: Identifying and analyzing long-term risks and taking steps to eliminate these risks if possible, or otherwise, reducing the likelihood and impact of these risks.
- Readiness, which involves developing systems and operational capabilities before an emergency occurs;
- Response, which is taking immediate action before, during, or after a significant event; and
- Recovery, which involves coordinated efforts and processes to promote short, medium, and long-term recovery.
In this meeting, Prof. Armaidy recommended the governance of National Security and National Resilience (Kamnas-Tannas), which includes strengthening the focus on national security risk management governance and the formation of national resilience, emphasizing the importance of strong relationships in governance, security and intelligence cohesion, as well as more effective Kamnas stakeholders.
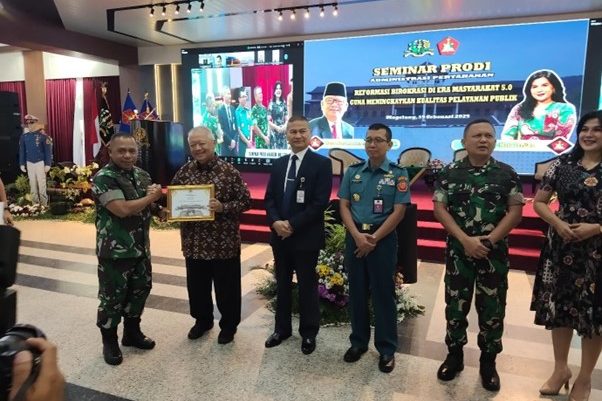
The seminar also featured Prof. Dr. Ir. H. Surachman Surjaatmadja, M.M, as the second speaker, along with Rear Admiral Dr. Sri Yanto, M.Si (Han), and Brigadier General Hary Murlyanto, M.Sc, with the session moderator Meta Tertina.
This activity aligns with the implementation of the SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals) including: Goal 1 No Poverty, Goal 2 No Hunger, Goal 3 Good Health and Well-being, Goal 4 Quality Education, Goal 11 Sustainable Cities and Communities, Goal 16 Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions, and Goal 17 Partnerships to achieve the goals.
Writer: Arni W
Editor: Ana Anggraini